
Scriptly Helps Pharmacies Identify Trends in Real Time with Reveal
A high-impact dashboard UI can be a daunting thing to design. Especially if you don’t know where to start. But following the dashboard design best practices that we list in this article makes the goal achievable.
Executive Summary:
A great embedded analytics solution can enhance data-driven decision-making and lead to improved outcomes with powerful, high-impact dashboards.
Too often, unfortunately, valuable business data is obscured by a bad presentation. Overcrowded dashboards with confusing and misleading information keep users from extracting actionable insights.
Dashboards and analytics are only useful when users can understand them.
This is where embedded analytics tools come in handy – they let you turn your data into a story with great visual UI elements and UX.
In this article, we’ll be sharing the core principles of creating high-impact UI/UX dashboards with embedded analytics to improve your end-user’s decision-making process for maximum profitability.
In a nutshell, UI (user interface) is the series of pages, screens, and visual elements that enable the user to interact directly with a product or service. On the other hand, UX (user experience) is a user’s complete experience when they interact with every aspect of a company’s product or service.
UI is anything that a user accesses and interacts with when using your product or service, including menus, buttons, forms, icons, images, typography, icons, search fields, etc.
UX encompasses every little detail and many user interfaces that roll up into one to form a seamless user experience for the end-users interacting with the product or service. These details include usability, function, ease of navigation, etc.
Despite the slight differences between UI and UX, both elements are crucial in product development and work closely together to determine how a product will look and function – with one influencing the other. There is no UI without UX and vice versa.
Imagine that you have created the most beautiful website, but then fail to realize that people find it hard to navigate and can’t find what they are looking for. Regardless of how beautiful the UI is, without a good UX, users will become frustrated and leave never to return to your website.
Dashboards are powerful tools to influence users’ decision-making processes. They help users get at-a-glance information on their most important KPIs and metrics and display relevant and actionable data. A high-impact dashboard is possible and can be created through dashboard UI design.
If you design a modern UI dashboard, you will provide your users with the data they need, in an easy-to-scan and understand format. Here are some other key benefits of a great dashboard UI:
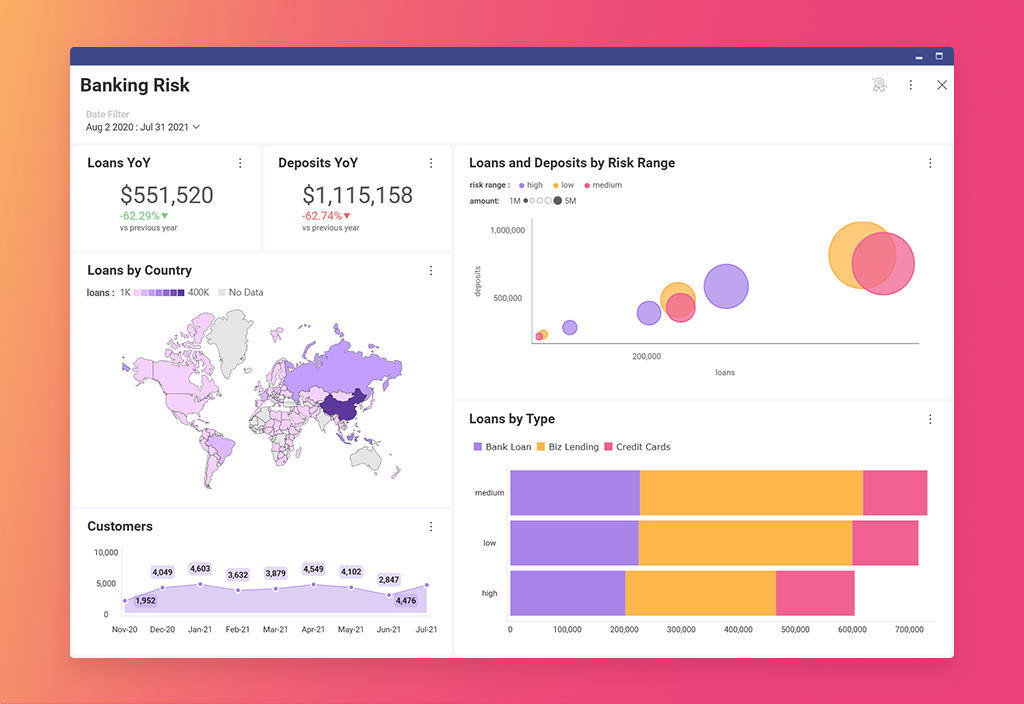
A high-impact dashboard UI can be a daunting thing to design. Especially if you don’t know where to start. But following the dashboard design best practices that we list below makes the goal achievable. To ensure you design a modern UI for your dashboard, follow these 12 UI/UX principles:
The dashboard has a specific purpose to serve, and if you get that wrong from the beginning, even if you follow all other dashboard design best practices, the result will be meaningless.
There are 4 dashboards categories to choose from:
Dashboards communicate data stories; the golden rule of communication is knowing your audience. To follow the principles of high-impact dashboard design, you need to identify your targeted audience – the people who will read the information you present within that dashboard.
You will communicate the dashboard data differently to a technical user than to a business user or if you are making a sales pitch to a client or a presentation to your company’s executives.
One of the biggest challenges of effective dashboard UI is picking out the right chart type to visualize the data to the audience you’ve already identified. There are infinite chart types to choose from, and each has unique attributes that can help you best get your message or data story across.
And while your data could work with multiple charts, it is up to you as the dashboard UI designer to make sure you select the chart type that makes the data clear and concise for your audience.
When choosing a chart type, think of these key questions:
Choose the point you want to make and select a chart type that is optimal.

While this might sound obvious, it is not – we’ve seen so many examples of dashboards full of distractive and unnecessary data and elements, haven’t we?
The challenge here is to find the balance between the data you CAN display on a dashboard and the data you SHOULD display on it. We know it might be tempting to add every possible chart and filter into your dashboard, but will that make it effective and high-impact – no!
Make it easy for your users to find more information by providing them with access to dive deeper into the data in another area of your product.
Based on the logic from our previous point, dashboards not only need to display the essential data while not overwhelming users, but they also need to strive for simplicity.
Make your dashboard UI/UX design intuitive. For example, place the sidebar on the left-hand side of the screen where users would expect to find it.
Also, we’ll touch on this shortly but don’t overdo colors, graphics, effects, etc. Dashboards don’t have to be impressive or amazing – they have to be efficient.
A good, high-impact dashboard will also include descriptive titles and descriptions to help users quickly understand the data and easily navigate the dashboard.
Use descriptive and concise titles that give the users reason and explanation for your chart. Keep your chart title simple and to the point since your data and visualization should tell the core of your story. Your title should directly relate to and support the chart underneath it.
Furthermore:
Colors can help you highlight what’s important or they can derail your dashboard. But when speaking of colors, we all have a wide array of preconceptions regarding different colors. For example, red is commonly seen as a bad sign, while green is commonly seen as a good sign.
Naturally, as you’re designing your dashboard, you have to consider this and remember to keep basic design psychology principles in mind.
However, to avoid chart confusion and derailing from your story, there are three types of color schemes you can use on your dashboards – diverging, sequential, and categorical.
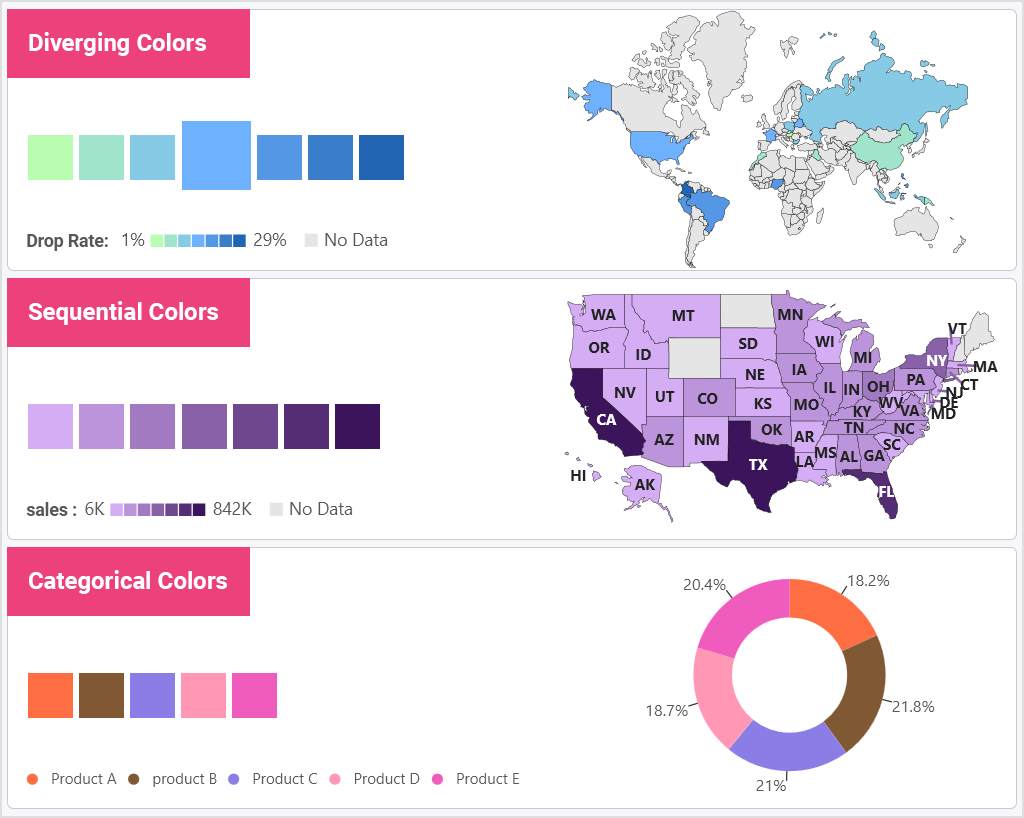
Design visualizations to focus the user on the most important thing about your data story. Highlighting key points, trends, and bounds within your data can be key to providing your end users with the quick insights they need.
Use these key features when looking to highlight important data:
Modern data analytics programs make it easy to create interactions to allow users to slice and dice data to gain deeper insights into the questions they are looking to answer.
Some of the most effective interactions include:
Dynamic filtering – adding filters to your dashboard or visualization allows you to pivot your data on the fly to gain deeper insights. Provide different options for your users to slice and dice data by category fields or date ranges, either at the dashboard or visualization level.
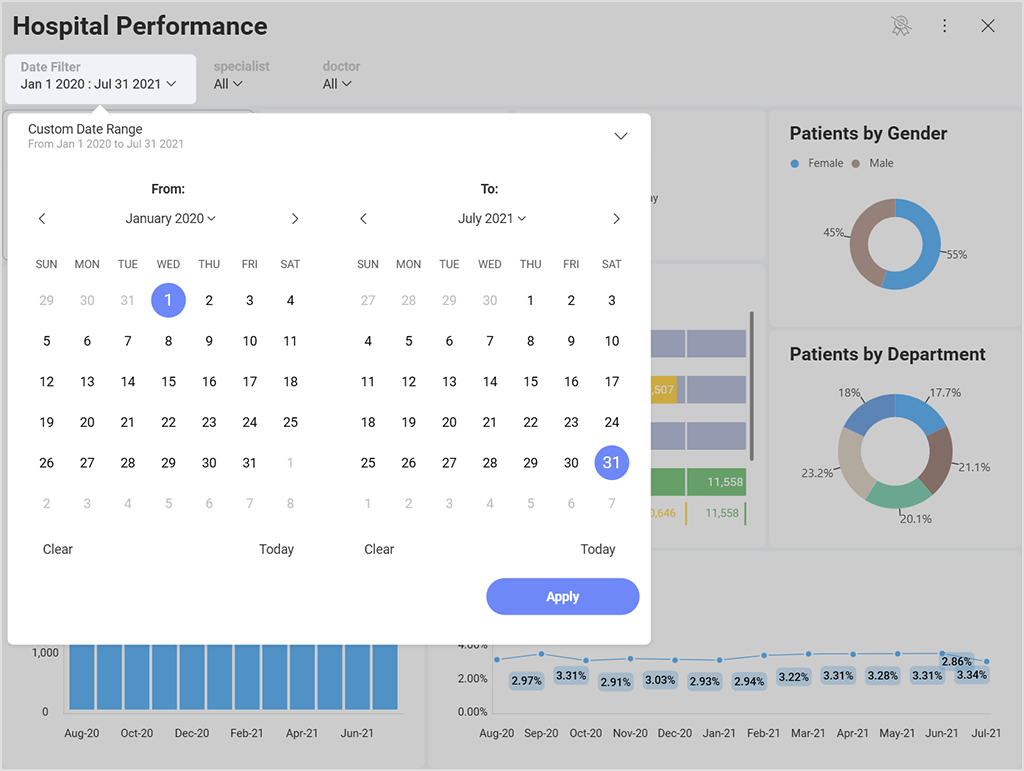
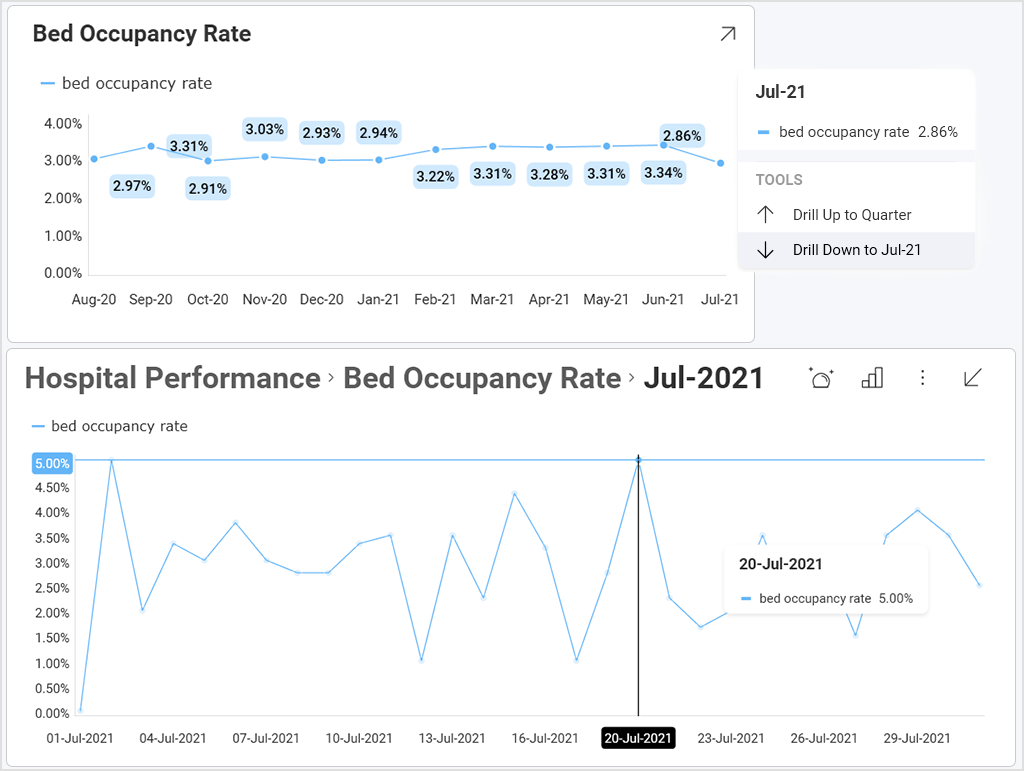
Drill-down – enabling hierarchies within your category or date fields allows your end-users to do deeper analysis.
Treemap – treemaps are excellent visualizations for drill-downs as they display large amounts of hierarchical data in a compact space at a glance, and they show data as part of a whole.
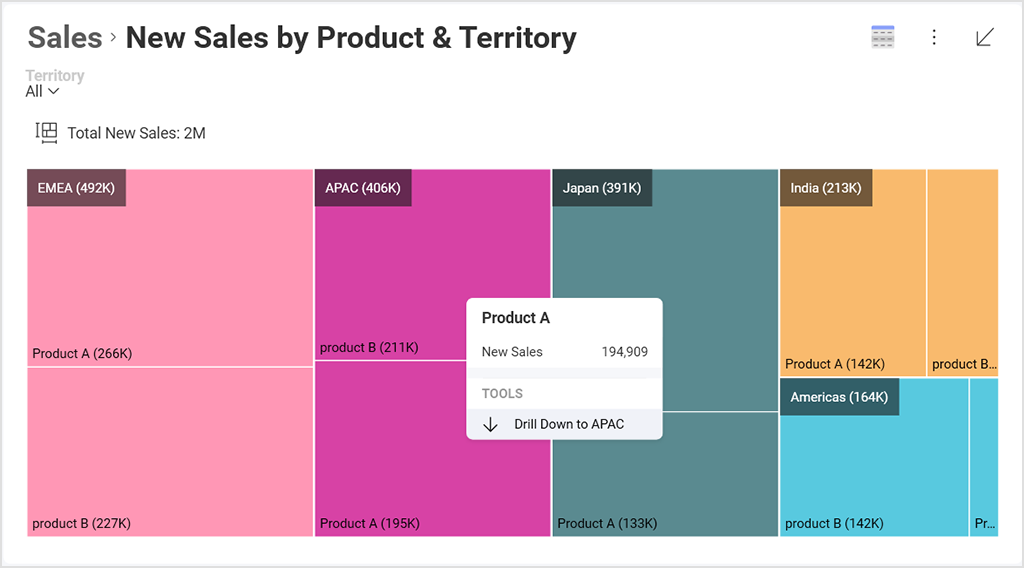
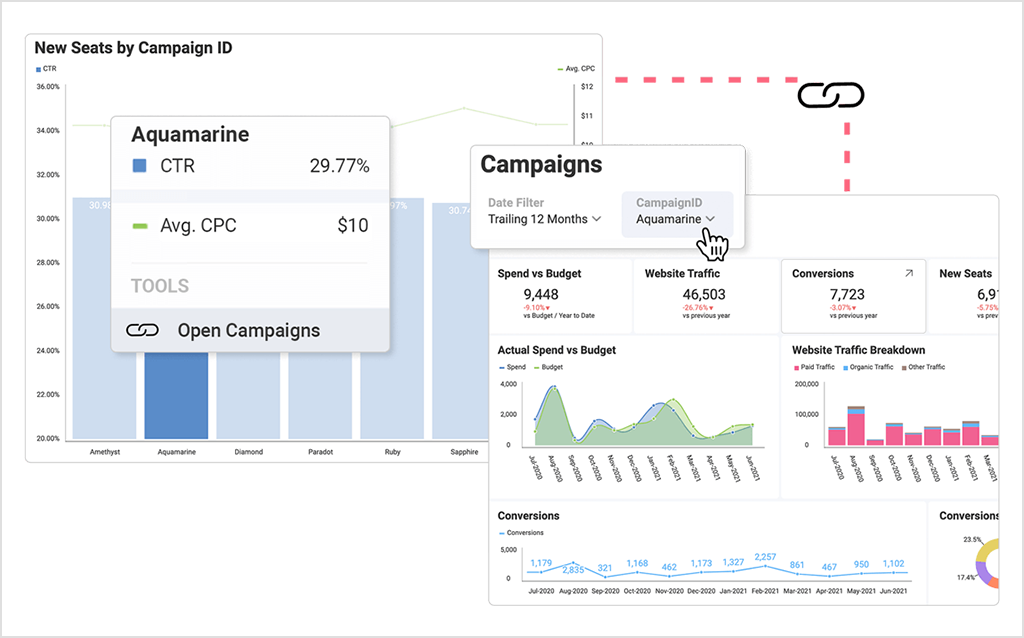
Dashboard linking – link data points or visualizations to other dashboards.
White spaces, also known as negative spaces, are the noticeable margins between metrics in your dashboard. The data story becomes hard to read if that white, negative space is not balanced.
Saving this area between the charts and elements of your dashboard will make it look wider and less overwhelming. You can use different views and data filters to double your margins and make it possible to display all the information on the same screen.
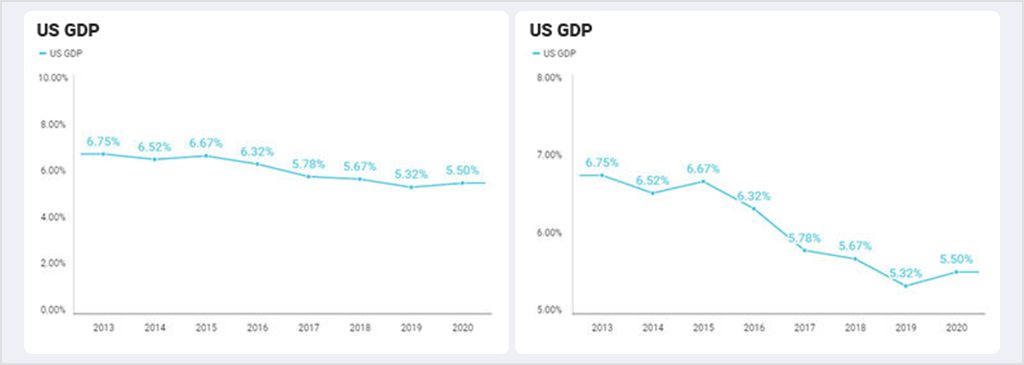
The scale for a graph axis can significantly impact how an audience interprets a message within the data story and is an important part of optimizing data visualization.
The best way to avoid being guilty of misleading visualizations is to steer clear of changing the scale of the Y-Axis. This tends to tell a different story than the data should.
Here’s just one example of how a chart tells an incorrect story. Both charts show the same data. However, the right chart has the axis starting at 5%, making it look like the US GDP is plummeting. Whereas when you look at the left chart, there is, in fact, only a small gradual decline.
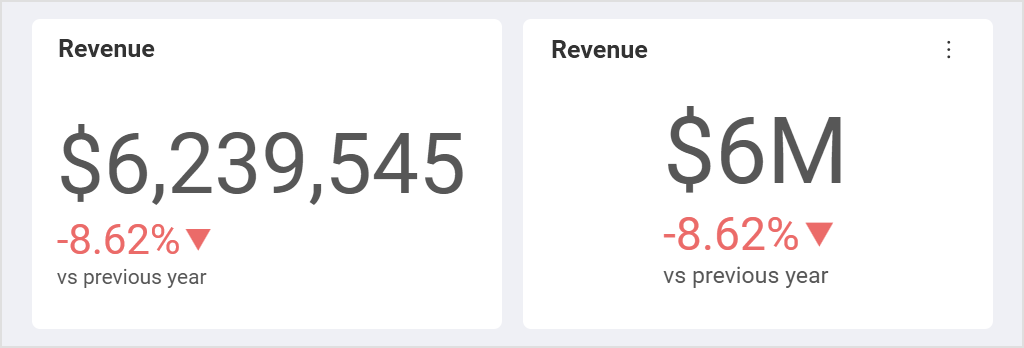
Sometimes details can enhance your dashboard UI/UX, but other times excessive detail confuses your message. For instance, keeping your numbers formatted or filtering out top results makes data more easily readable.
Formatting your data can be a quick, simple way to make the numbers more visually appealing and easier for an end-user to read. For either gauges or charts such as bar charts and column charts, you can adjust your data formatting to make your data point stand out: limiting the number of decimals, for example, or adjusting the placement of comma separators. Also, consider using currency, percentage measurements, or large number formatting.
You have probably heard about embedded analytics and the booming demand for business intelligence insights that are derived from it. A recent survey by Reveal showed that embedded analytics platforms are soaring in popularity for their ability to make data-driven decisions, gain a competitive advantage and drive sales –with 58% of respondents embedding analytics in their apps for their own use in 2022, in comparison to 33% in 2021.
The primary reason for that is that embedded analytics platforms improve business decisions through high-impact dashboards. Embedded analytics brings real-time, interactive data visualizations and dashboards, and business intelligence capabilities directly into users’ workflow – creating contextual data that improves the usability of data for business users.
Providing users with relevant and timely insights within their workflow promotes a data-driven culture and encourages more analytical thinking. In-context analytics will enable your users to make faster and more intelligent decisions that are based on the information available at that moment or visible on the specific screen they are viewing.
Furthermore, a good embedded analytics solution comes with self-service capabilities that provide intuitive UI, making interacting with data more accessible for those who don’t have technical knowledge. With self-service capabilities, users can independently access and analyze data by themselves and build informative high-impact dashboards and reports.
Reveal is an end-to-end self-service embedded analytics solution that brings the power of data into the hands of your employees, customers, partners, and suppliers. At its core, Reveal is centered around data-driven decision-making, and it has been designed to allow you to easily integrate interactive dashboards and data visualizations, white-label capabilities, advanced and predictive analytics, including machine learning, forecasting, statistical functions, and more into your apps, so your users can access real-time insights and build beautiful and informative dashboards anywhere and on any device.
You can learn more about Reveal and how it work by downloading our SDK or by scheduling a quick demo.
Back to Top